Synthetic data augmentation for robotic mobility aids to support blind and low vision people
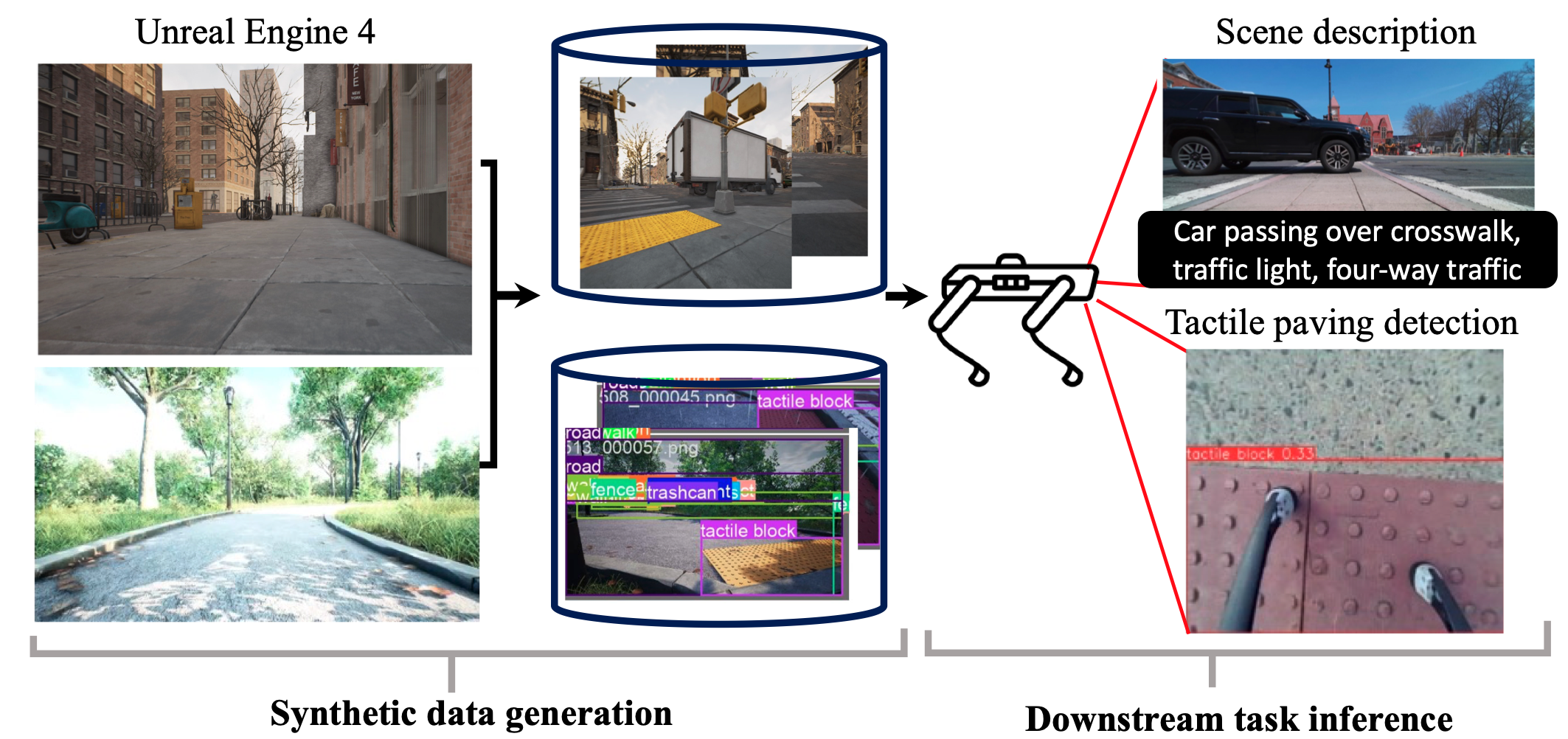
Abstract: Robotic mobility aids for blind and low-vision (BLV) individuals rely heavily on deep learning-based vision models specialized for various \ navigational tasks. However, the performance of these models is often constrained by the availability and diversity of real-world datasets, which are challenging to collect in sufficient quantities for different tasks. In this study, we investigate the effectiveness of synthetic data, generated using Unreal Engine 4, for training robust vision models for this safety-critical application. Our findings demonstrate that synthetic data can enhance model performance across multiple tasks, showcasing both its potential and its limitations when compared to real-world data. We offer valuable insights into optimizing synthetic data generation for develop- ing robotic mobility aids. Additionally, we publicly release our generated synthetic dataset to support ongoing research in assistive technologies for BLV individuals, available at [Download]
Summary
We generated synthetic data using Unreal Engine 4 and the NVIDIA Deep Learning Dataset Synthesizer for various nav- igational downstream tasks. The key contributions of our work can be summarized in threefolds:
- We propose a pipeline for generating synthetic data tailored for training deep learning models used in robotic mobility aids.
- We demonstrate the effectiveness of synthetic data in fine-tuning models for downstream tasks, showing improved performance in tactile paving detection and scene description.
- We share a comprehensive synthetic dataset that includes a wide range of scenarios, enhancing the robustness of models across various tasks.
Synthetic data generation environment
The Suburban environment features urban roads and sidewalks that contain a variety of objects commonly found in sidewalk settings. Controllable camera trajectories allow data collection from diverse viewpoints, reflecting the perspectives of different robotic mobility aids.
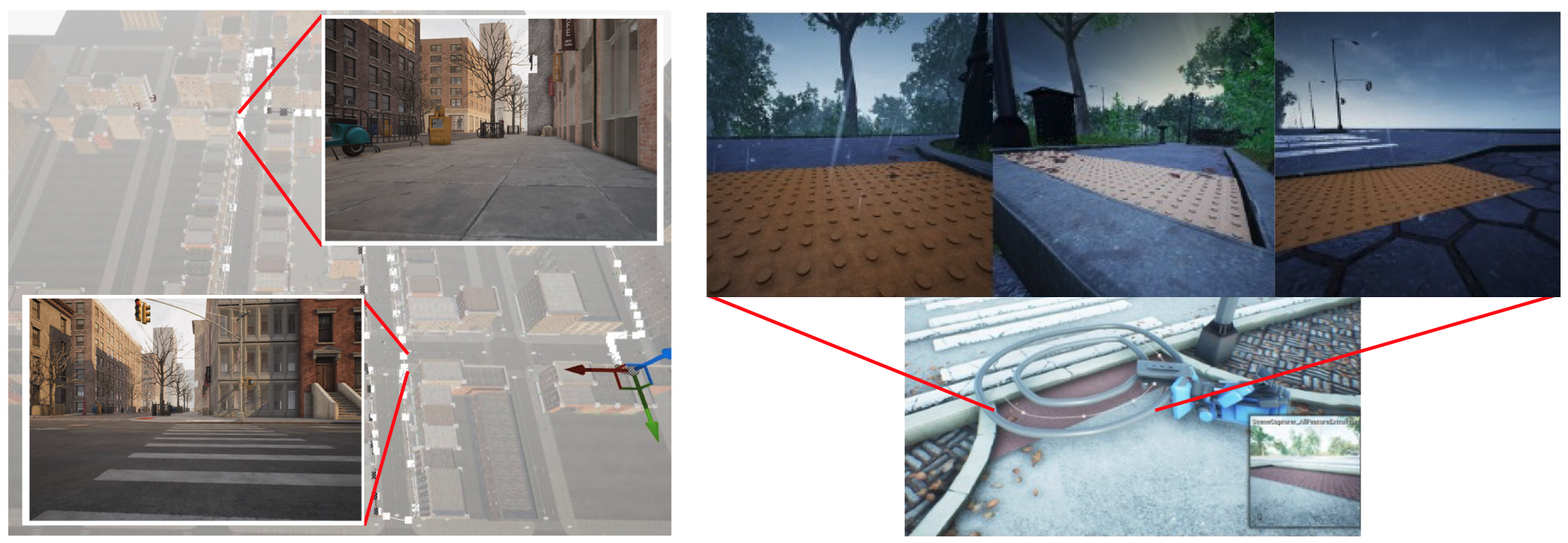

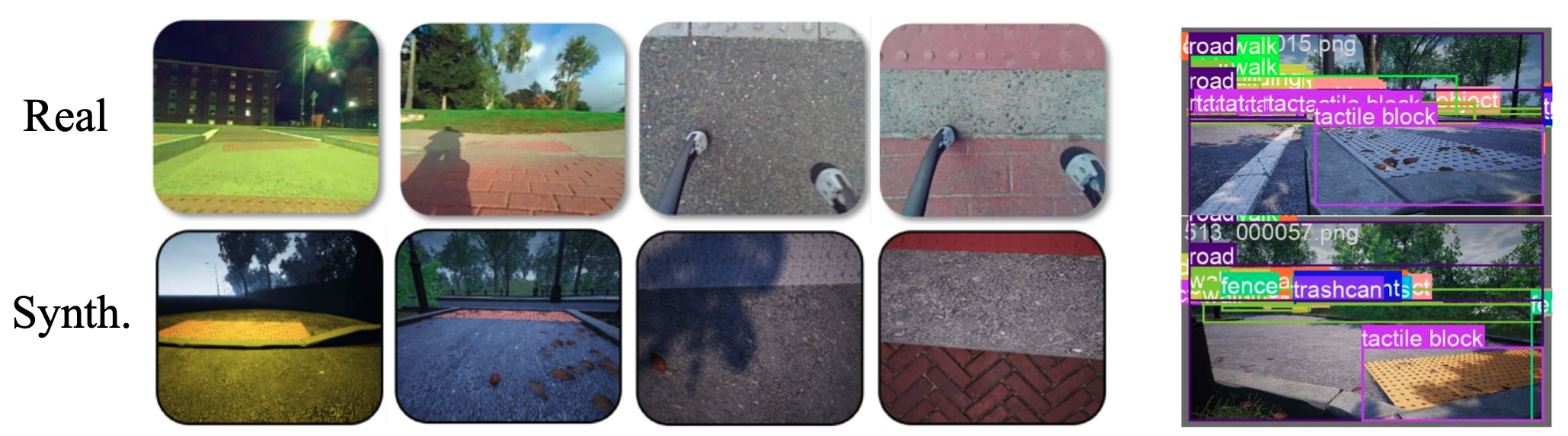
Synthetic Tactile-on-Paving (SToP) Dataset
Comparison between real data and gen- erated synthetic data in various lighting and viewpoint settings, highlighting the close resemblance of synthetic data to real-world conditions. Visualization of ground truth bounding boxes within the UE4 environment.

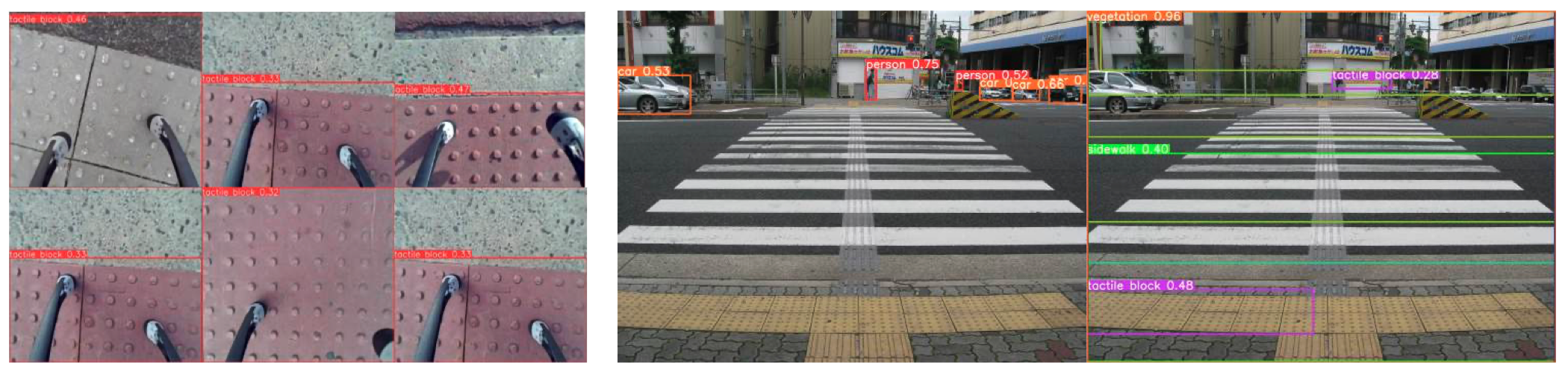
Experimental Results 1: Tactile paving detection
To evaluate the SToP dataset, we fine-tuned YOLOv8 and YOLO-World specifically for tactile paving detection.
- (Left) YOLOv8 successfully detects tactile pavings from a top-down view, which were not detected by the pretrained model with- out synthetic data training.
- (Right) The open-vocabulary YOLO-World provides bounding boxes for tactile pavings, a capability that was not achieved previously (Center) on a publicly available dataset.

Experimental Results 2: Scene description
For the scene description task, we fine-tuned the Florence-2 vision foundation model using our synthetic street crossing dataset, complemented by text annotations crafted by one of the researchers to reflect the informational prefer- ences of BLV individuals during street crossings. As shown in Table 1, incorporating additional real-world and synthetic data led to comparable performance improvements over the baseline, except for precision. Qualitative results of the fine-tuned Florence-2 model are presented in Table 2, where the model exhibited strong performance in generating accurate descriptions across varied conditions, though some inaccuracies and missing information were found.
